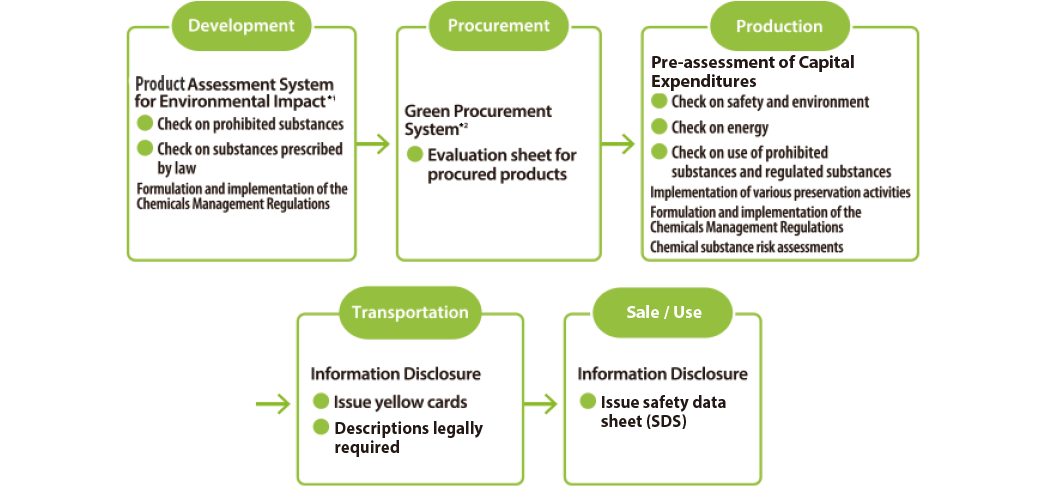
Chemical Substance Management
Minimizing Environmental Impact through Proper Control and Reduction of Chemical Substance Emissions
Minimizing Environmental Impact through Proper Control and Reduction of Chemical Substance Emissions
While chemical substances make people’s lives more convenient, they also could have harmful effects on the environment or on human beings. Therefore, we believe that taking into consideration product safety, occupational safety and health, and environmental impact through the proper management of chemical substances is an important responsibility.
Since fiscal 1999, SEKISUI CHEMICAL Group has set and worked toward its own targets for reducing emissions and the transfer of chemical substances in addition to implementing efforts such as the Product Assessment System for Environmental Impact*1 and the Green Procurement System*2. Periodically we also review chemical substances, in accordance with the establishment and amendment of relevant laws and regulations.
From fiscal 2021, we will continue to engage in thoroughgoing chemical substance management activities with an awareness of minimizing their impact.
-
*1Product Assessment System for Environmental Impact: A system for assessing the environmental impact of products at all stages from raw material procurement through manufacture, use, disposal, and transportation.*
-
*2Green Procurement System: A system which prioritizes lower levels of environmental impact when procuring raw materials, parts, etc.
- 11-92
Controlling VOC Emissions
SEKISUI CHEMICAL maintains the medium-term target of reducing VOC emissions by 3% or more compared with the fiscal 2019 level. In fiscal 2021, VOC emissions in Japan decreased by 6.7% compared with fiscal 2019.
Preventing Air and Water Pollution
SEKISUI CHEMICAL Group complies with laws and ordinances for equipment related to exhaust gases and water drainage.
Soil Contamination Countermeasures
SEKISUI CHEMICAL Group conducted a voluntary assessment of soil contamination at all of its production sites. The Group has implemented cleanup measures and efforts aimed at preventing further contamination at all locations where contamination was found while completing its report to the government. In addition, the Group continuously monitors groundwater, confirming that pollution is not spreading.
Moreover, the Group takes legally mandated decontamination measures when selling land on which production facilities have been closed. In fiscal 2021, conditions did not require any new measures to be taken.
Disposal and Storage of Devices Containing PCBs and Management of Equipment That Uses Fluorocarbons
Transformers and capacitors that contain PCBs are being removed sequentially as PCB treatment facilities are ready to accept taking our equipment. Control of equipment containing PCBs in storage is strictly enforced, including locking of storage facilities and periodic inspections.
Steps are being taken to enhance awareness toward mandatory requirements regarding equipment that use fluorocarbons in accordance with Japan’s Act on Rational Use and Proper Management of Fluorocarbons (Freon Emission Control Act) and to ensure thoroughgoing management including periodic inspection.
For more details, see Products to Enhance Sustainability
-
Note:From fiscal 2019, results from the medical business are collated and presented with Corporate Headquarters results following its separation from the HPP Company.
Aggregated results based on the PRTR Law
(substances handled at business sites subject to assessment with a handling volume of 1 ton or more are aggregated).
| Substance | Govt. ordinance notification no. |
Emission volume |
Emission volume | Transfer volume | Detoxification | |||||
| Atmospheric | Public water areas |
In-house soil | In-house landfill |
Sewage system |
Transfer in waste disposal | Transfer in waste recycling | ||||
| Ethyl acrylate | [3] | 36.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.66 | 33.0 |
| Acrylic acid and its water solvent | [4] | 1.3 | 0.061 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.13 | 0 | 1.065 |
| n-Butyl acrylate | [7] | 202.2 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.4 | 0.0020 | 199 |
| Acrylonitrile | [9] | 482.1 | 4.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0090 | 478 |
| Acetaldehyde | [12] | 207.1 | 0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 207 |
| Acetonitrile | [13] | 53.9 | 4.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| 2,2’-Azobisisobutyronitrile | [16] | 5.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.8 |
| Antimony and its compounds | [31] | 10.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 | 0 |
| Isobutyraldehyde | [35] | 70.0 | 1.64 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 68 |
| 2-Ethylhexanoic acid | [51] | 5,720.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.9 | 5,706 |
| Ethylenediamine | [59] | 3.0 | 0.290 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.739 |
| ε-Caprolactam | [76] | 33.0 | 0 | 0.011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 |
| Xylene | [80] | 13.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 |
| Chromium and trivalent chromium compound | [87] | 3.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.044 | 0 |
| Vinyl chloride | [Special 94] | 125,314.4 | 4.0 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 125,310 |
| Chloroform | [127] | 7.0 | 0.37 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.0 | 0.71 |
| Cobalt and cobalt compounds | [132] | 3.1 | 0 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.9 |
| Vinyl acetate | [134] | 53.5 | 5.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.9 | 0.001 | 45 |
| "Inorganic cyanide compounds (not including complex salts and cyanate)" |
[144] | 21.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 22 |
| Cyclohexylamine | [154] | 8.2 | 0.46 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.8 |
| Methylene chloride | [186] | 360.3 | 4.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 356 |
| Divinylbenzene | [202] | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 |
| 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-cresol | [207] | 11.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11.3 |
| N,N-dimethylformamide | [232] | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.9 | 0 |
| Organic tin compounds | [239] | 148.9 | 0 | 0.0003 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.55 | 3 |
| Styrene | [240] | 1,193.8 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 422 |
| Tolylene Diisocyanate | [298] | 9.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Toluene | [300] | 623.3 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25.2 | 111 | 322 |
| Lead compounds | [Special 305] | 481.7 | 0 | 0.0026 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.3 | 57 |
| Nickel compound | [Special 309] | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bis-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | [355] | 4.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 | 0 |
| n-Hexane | [392] | 109.8 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 97 | 0 |
| Boron and its compounds | [405] | 55.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| "Poly (oxyethylene) = alkyl = ether (C = 12-15 and other blends)" |
[407] | 3.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Manganese and its compounds | [412] | 6.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.2 | 0 |
| Methacrylate | [415] | 265.4 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.012 | 264 |
| Methyl methacrylate | [420] | 184.8 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 183 |
| Methylnaphthalene | [438] | 1.3 | 0.0063 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 |
| Methylenebis (4,1-phenylene) = diisocyanate | [448] | 1,576.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0010 | 1,572 |
| 137,291.4 | 115 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30.6 | 287 | 135,330 | ||
| Index | Calculation Method |
|---|---|
| Amount of Chemical Substances Handled | Amount of substances subject to regulation by the PRTR Law handled [Scope: Production sites and research facilities in Japan] |
| Amount of Emissions / Transfer of Chemical Substances | Amount of emissions / transfer of chemical substances subject to regulation by the PRTR Law: Amount of emissions = Amount of emissions into the air + Amount of emissions into public waters + Amount of emissions into the soil on-site + Amount disposed of by landfill on-site Transfer amount = Amount transferred to sewers + Amount transferred as waste material [Scope: Production sites and research facilities in Japan] |
| Amount of Chemical Substances Subject to Detoxication | Amount of chemical substances subject to regulation by the PRTR Law subject to detoxication: Amount detoxified = Amount consumed in reaction + Amount consumed through combustion, etc. [Scope: Production sites and research facilities in Japan] |
- 11-95
- 11-96
-
Amount of Chemical Substance Emission and Transfer (PRTR Law) / Japan
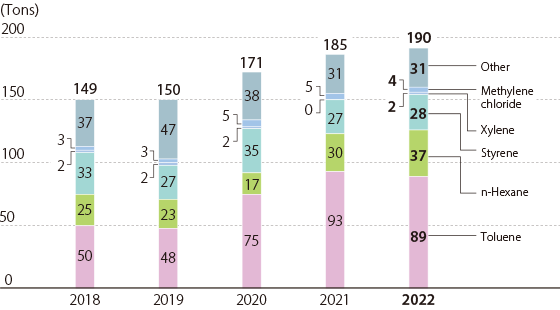
-
Note:Past figures have been retroactively revised due to changes in aggregate scope.
Index Calculation Method Amount of Emissions / Transfer of Chemical Substances Amount of emissions / transfer of chemical substances subject to regulation by the PRTR Law: Amount of emissions = Amount of emissions into the air + Amount of emissions into public waters + Amount of emissions into the soil on-site + Amount disposed by landfill on-site
Transfer volume = Amount transferred to sewers + Amount transferred as waste material
Scope: Covers production sites and research facilities in Japan -
-
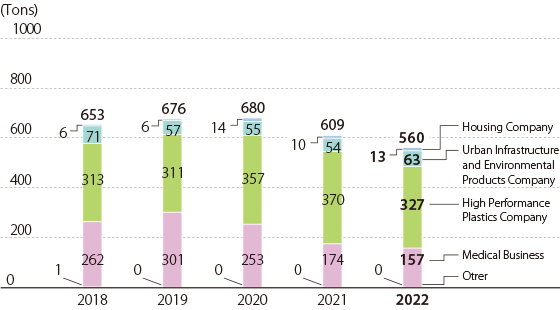
Discharge of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) into the Atmosphere / Japan
-
Note:Past figures have been retroactively revised due to changes in aggregate scope.
Index Calculation Method VOC Emissions Amount of emissions into the atmosphere of volatile organic compounds (VOC) among the substances subject to regulation by the PRTR Law and Japan Chemical Industry Association -
- 11-99
- 11-100
-
NOx Emissions / Japan
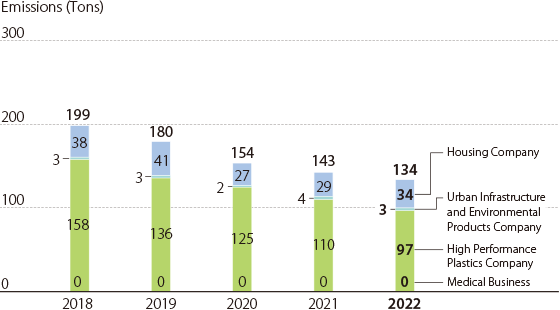
Index Calculation Method NOx Emissions NOx emissions =Σ(Amount of exhaust gas airflow per year x NOx concentration x 46/22.4) -
SOx Emissions / Japan
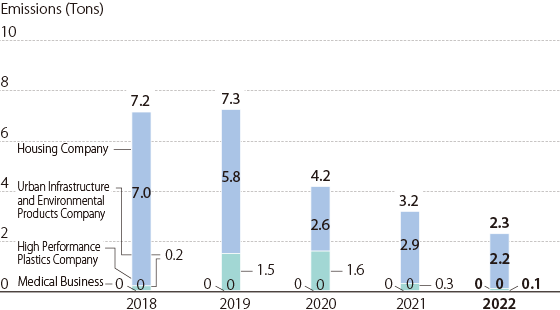
Index Calculation Method SOx Emissions SOx emissions =Σ(amount of SOx per year x 64/22.4)
- 11-103
-
Soot and Dust Emissions / Japan
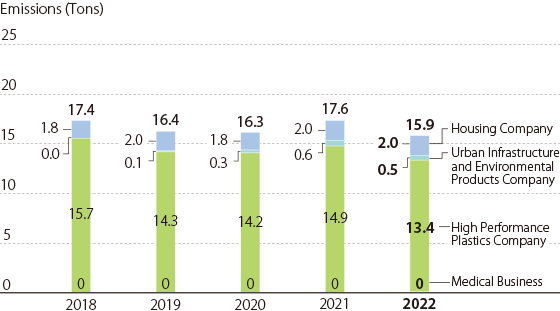
Index Calculation Method Soot and Dust Emissions Soot and Dust emissions =Σ(amount of exhaust gas airflow per year x soot concentration)
