-A new high stiff material that is lighter than metal and uses graphene-like carbon-
--Possesses the same stiffness at 1/3 the weight of a steel plate, and high designability due to its excellent thermoforming--
Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd. (President: Naofumi Negishi, hereinafter called
"Sekisui Chemical")'s High Performance Plastics Company (President:
Keita Kato) has developed a layered "high stiff lightweight resin sheet"
from reinforced resin sheets that combine graphene-like carbon, and polyolefin
foam.
Using the combined characteristics of lightweightness and high stiffness
that cannot be achieved with metals will in future promote a wide range of applications
and development in such fields as Buildings and Infrastructures, Automobiles
and Transportation.
1. Background to the Development
Sekisui Chemical cites the opening of such frontiers as "Creation of
Housing/Social Infrastructure" and "Chemical Solutions" in its
group vision for the High Performance Plastics Company to supply various plastic
products in strategic fields such as Buildings and Infrastructures, Automobiles
and Transportation, Electronics, and Life Sciences.
Therein, we became
involved in the development of new lightweight materials from which environmental
contributions are expected.
2. Overview of "High Stiff Lightweight Resin Sheets"
1. Structure and Performance
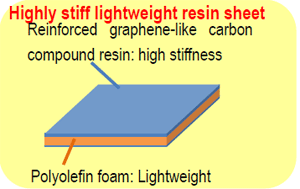
As shown in the diagram below, the developed product, "high Stiff lightweight resin sheets", has an outer layer of reinforced resin sheets, which combine graphene-like carbon*, and an intermediate layer of polyolefin foam for a 3-layer configuration.
|
|
*Graphene-like carbon |
|
|
|
|
|
Fig.: Configuration of high stiff lightweight resin sheets |
|
Photo: Mold example |
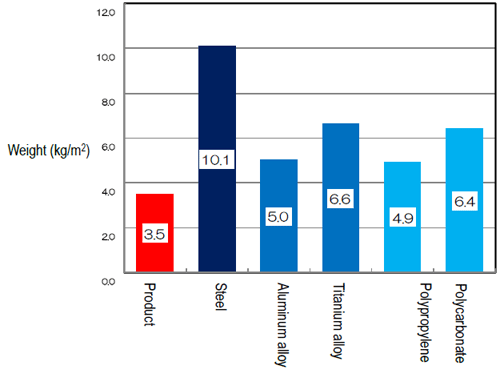
The possession of this layered configuration enables both lightweightness and high stiffness, and as shown in the graph below, achieves the same stiffness with only 1/3rd the weight of steel plates.
|
|
|
Graph: Required weight to manifest the same stiffness |
Further, the main component of the "high stiff lightweight resin sheets"
is thermoplastic resin, and so has excellent designability with easy heat molding
such as press molds, etc., in the same way as regular plastic and differing
from reinforced carbon fiber resin and reinforced glass fiber resin.
2. Specification Examples
Representative examples of the product specifications are shown in the table below. Type A focuses on stiffness, and Type B grades focus on lightweightness. In this way, it is possible to design a broad range of qualities tailored to the application, and the resin materials also have a high standard of shock resistance.
|
Physical Property |
Unit |
Type A |
Type B |
|
Lightweightness(Weight) |
g/m2 |
3500 |
2200 |
|
Stiffness(Strain gradient) |
N/cm/5cm |
750 |
550 |
|
Sheet Thickness |
mm |
10max. |
10max. |
3. Future Developments
In future, Sekisui Chemical will be involved with commercialization by promoting links with a broad range of business partners with the aim of developing applications in various fields such as Buildings and Infrastructures’ materials including architectural and civil engineering materials, and Automobiles and Transportation such as ships, aircraft, and railroads, etc. Further, as well as promoting the technical development of mass production, Sekisui Chemical also plans to supply product samples of the "high stiff lightweight resin sheets" in the summer of 2015.
Disclaimer
This press release may contain forward-looking statements. Such forward-looking statements are based on current expectations and beliefs and are subject to a number of factors and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such statements due to changes in global economic, business, competitive market and regulatory factors.